Wool has shaped human history for over 8,000 years. From ancient sheep domestication in 6000 BCE to its central role in medieval economies and the Industrial Revolution, wool has been prized for its warmth, durability, and versatility. Today, it remains a sustainable choice in modern fashion.
Key Takeaways:
- Origins: Wool production began around 6000 BCE in the Near East, evolving with selective sheep breeding.
- Medieval Trade: Wool dominated Europe's economy, particularly in Britain, despite challenges like the Black Death.
- Industrial Revolution: Inventions like the spinning jenny and power loom transformed wool production into a global industry.
- Modern Use: Wool is eco-friendly, biodegradable, and used in everything from performance wear to business suits.
Wool's journey highlights its enduring impact on societies, economies, and fashion. Keep reading to explore its fascinating evolution.
The Timeless Impact of Sheep's Wool on Human Civilization
The Origins of Wool
How Sheep Were Domesticated
Around 6000 BCE, humans in the Near East began raising sheep, initially focusing on their meat and milk [4]. Over time, selective breeding led to sheep with thicker, woollier coats, making them ideal for textile production [2]. As domestication spread across the globe, different breeds emerged, suited to local climates and needs. Ancient communities in Iran played a key role in refining wool processing techniques, which became the foundation for textile production [2]. This shift from using sheep mainly for food to creating textiles marked a major turning point in human history.
The First Wool Textiles
Archaeological findings in Southern Turkey show that woolen garments were in use as early as 6000 BCE, offering a glimpse into wool's early role in human society [3]. Using tools like the distaff and spindle, early civilizations such as the Sumerians and Egyptians turned raw wool into textiles. These ranged from simple everyday clothing to elaborate garments that symbolized social status [4][3].
Different cultures made unique contributions to wool's development. The Sumerians established early trade systems for wool, Egyptians crafted fine textiles that have been preserved in tombs, and Mongolians developed methods to produce wool suited to harsh climates [4][3]. While these early textiles were coarser than what we know today, they were highly valued for their warmth and durability. Transforming raw wool into fabric required advanced techniques [4][3], which paved the way for centuries of textile innovation. Beyond meeting practical needs, wool became a key commodity in early trade networks, shaping economies and cultures.
These early breakthroughs in wool production laid the foundation for its lasting importance in trade and cultural exchange.
Wool's Impact on Societies and Economies
The Wool Trade in Medieval Europe
In medieval Europe, wool played a pivotal role in Britain's economy. Areas like Yorkshire and the Cotswolds became renowned for sheep farming, while cities such as York and Norwich emerged as key trading centers. Guilds oversaw the quality and regulation of the wool trade, ensuring its success. Even with obstacles like the Black Death and competition from Spanish Merino wool, Britain adjusted by focusing on domestic cloth production, maintaining its dominance in textiles [1].
While Europe thrived on wool trade, other parts of the world forged their own connections with this versatile material.
Wool in Different Cultures
Globally, wool has taken on unique roles in various cultures and economies. In Mongolia and Tibet, yak and sheep wool were essential for crafting traditional clothing and building shelter to endure harsh climates [4]. Meanwhile, Australia's introduction of Merino sheep in 1797 transformed its economy, propelling the country to the forefront of premium wool production [2]. These developments highlight wool's ability to meet diverse needs while shaping societies and economies around the world.
These regional advancements laid the groundwork for the Industrial Revolution, which would forever change how wool was produced on a global scale.
Advances in Wool Production
The Spinning Wheel and Early Tools
The spinning wheel, introduced during the Middle Ages, brought a major leap forward in wool production by making spinning much faster and more efficient [4][5]. Before its invention, people relied on simple hand tools that, while useful for their time, could only produce limited amounts of yarn. The spinning wheel marked a turning point, allowing for quicker and more uniform yarn production, which was a game-changer for textile manufacturing.
Wool Production During the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution completely changed the wool industry with inventions like James Hargreaves' spinning jenny in 1764 and Edmund Cartwright's power loom in 1787 [1]. The spinning jenny allowed one worker to operate several spindles at once, while the power loom automated the weaving process. These innovations shifted wool production from small-scale, home-based operations to large industrial factories, especially in British regions like Yorkshire and Lancashire [1].
Here's a quick look at some of the key tools and their impact:
| Innovation | Year | Impact on Wool Production |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Spindles | ~6000 BCE | The first tool used for wool textiles |
| Spinning Wheel | 14th Century | Made yarn spinning faster and uniform |
| Spinning Jenny | 1764 | Enabled one worker to spin multiple spindles |
| Power Loom | 1787 | Automated the weaving process |
These breakthroughs not only made wool fabrics more affordable and widely available but also solidified wool's role as a staple in textile production [1][5]. By boosting efficiency, these tools set the stage for wool's continued importance, even as modern practices focus on sustainability in the textile industry.
Wool in Today's Fashion Industry
Why Wool is Better for the Environment
Wool stands out as an eco-friendly material in fashion. Unlike synthetics that release microplastics into the environment, wool requires less water and energy to produce and breaks down naturally in soil when discarded [2][4].
Its benefits extend beyond production. Wool's durability aligns well with sustainable consumption habits, making it a practical choice for environmentally conscious consumers [2].
| Environmental Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint | Accounts for less than 2% of global agricultural emissions |
| Water Usage | Needs very little water for processing |
| Biodegradability | Breaks down naturally in soil |
| Chemical Usage | Requires minimal chemical treatment |
These advantages have made wool a go-to material for a variety of modern clothing needs.
How Wool is Used in Clothing Today
Wool’s adaptability makes it a staple in many types of clothing. Known for its excellent insulation, wool can absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture while staying breathable [2].
Here’s how wool is being used in the fashion industry today:
- Performance Wear: Merino wool is a favorite for athletic and outdoor gear, thanks to its ability to wick moisture.
- Business Attire: Lightweight wool suits provide natural temperature regulation.
- Casual Wear: Advances in processing have made wool softer and more comfortable for everyday clothing.
New England Woolens: A Modern Example
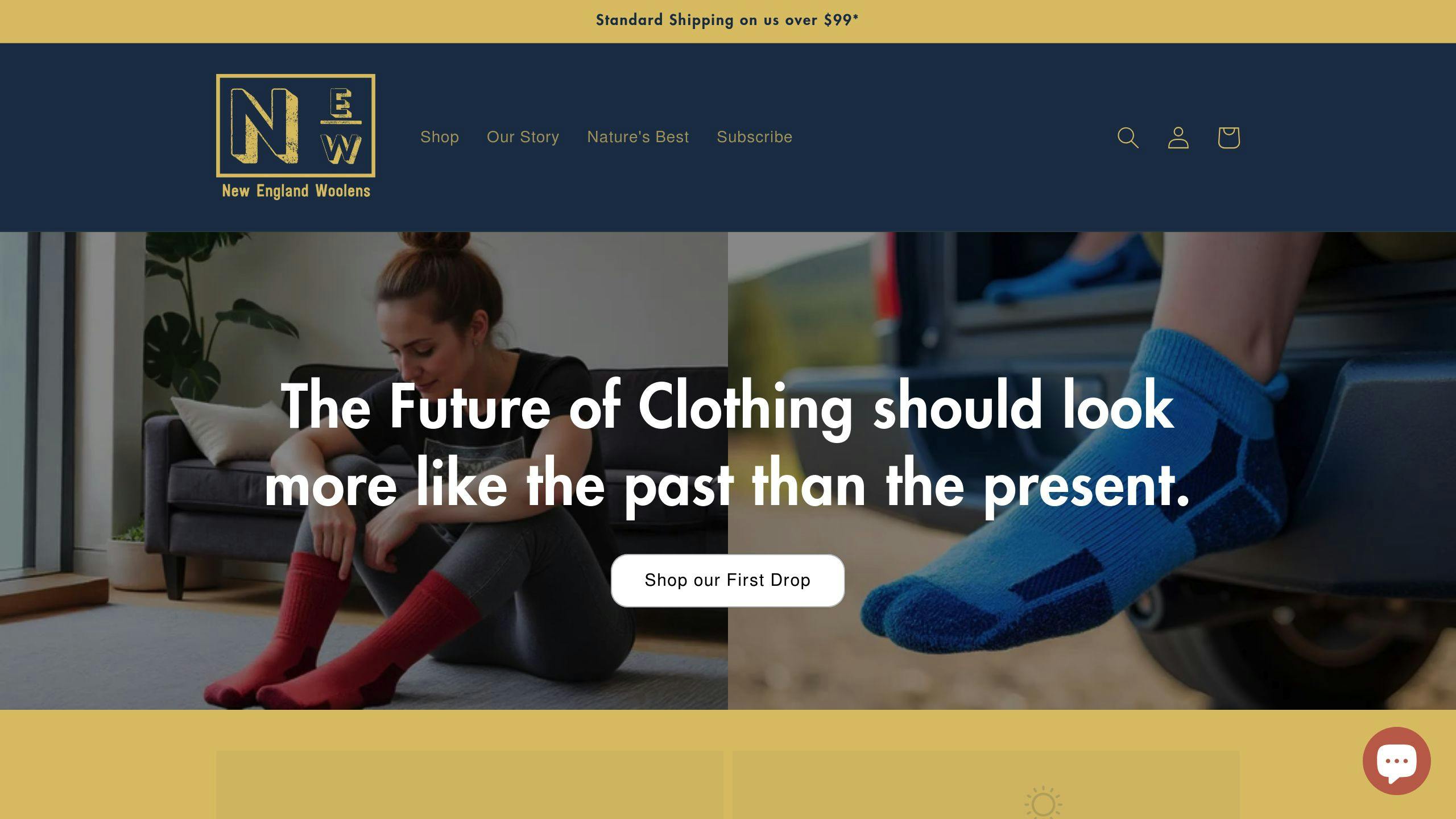
New England Woolens showcases how traditional wool craftsmanship can meet modern sustainability goals. Their ECO-TRAIL Merino Wool Hiker Socks blend merino wool with recycled nylon, combining high performance with eco-conscious design. Similarly, their All Day Alpaca Crew Socks highlight wool’s versatility in today’s fashion.
This brand’s success reflects the rising demand for sustainable wool products. By manufacturing in the USA and using natural fibers, New England Woolens demonstrates how wool can remain a key player in sustainable fashion, proving its relevance in the ever-evolving industry.
Conclusion: Wool's Journey Through Time
What We Learned About Wool
The Industrial Revolution changed the game for wool production, making it quicker and more accessible to people worldwide [1]. Shifting from small-scale cottage industries to large-scale manufacturing reshaped how wool was processed and distributed, making wool products available to a much broader audience [1]. Thanks to technological progress and updated production methods, wool has consistently evolved to meet society's needs, all while retaining its core characteristics [4].
The Future of Wool in Fashion
Wool's role in sustainable fashion is set to expand. Today, traditional techniques blend with modern technology to keep wool relevant for contemporary fashion needs [4]. Since the introduction of Spanish Merino sheep to Australia in 1797, the Australian wool industry has led the way in quality and innovation [2].









